GET 10% OFF YOUR FIRST ORDER
🧩UNDERSTANDING AND LOVE🧩
UNDERSTANDING AUTISM
7 Signs of Undiagnosed Autism in Adults
🧩AUTISM FACTS AND HELP🧩
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF AUTISM🧩
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF AUTISM🧩
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF AUTISM🧩
How do genetic and environmental influences give rise to autism?
Most appear to affect crucial aspects of early brain development. Many autism risk genes influence other networks of genes, increasing or decreasing their expression. Some appear to affect how brain nerve cells, or neurons, communicate with each other. Others appear to affect how entire regions of the brain communicate with each other. Research continues to explore these differences with an eye to developing interventions and supports that can improve quality of life.
Do vaccines cause autism?
Vaccines do not cause autism. It is possible that the timing of an autism diagnosis might coincide with the recommended vaccine schedule for children and adolescents. But scientists have conducted extensive research over the last two decades to determine there is no link between childhood vaccinations and autism. The results of this research is clear: Vaccines do not cause autism. Additionally, vaccination can protect children from many preventable diseases like measles.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has compiled a comprehensive list of this research.
Is autism genetic?
Research tells us that autism tends to run in families, and a meta-analysis of 7 twin studies claim that 60 to 90% of the risk for autism comes from your genome. If you have a child with autism, you are more likely to have another autistic child. Your other family members are also more likely to have a child with ASD.
Changes in certain genes or your genome increase the risk that a child will develop autism. If a parent carries one or more of these gene changes, they may get passed to a child (even if the parent does not have autism). For some people, a high risk for ASD can be associated with a genetic disorder, such as Rett syndrome or fragile X syndrome. For the majority of autism, multiple changes in other regions of your DNA increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder. The majority of these DNA changes do not cause autism by themselves but work in conjunction with many other genes and environmental factors to cause autism.
If you or your child has ASD, we recommend that you explore genetic testing. Genetic testing could show you the genetic cause of you or your child’s autism and reveal any genetic mutations that might be linked to serious co-occurring conditions like epilepsy. Genetic testing can give doctors useful information so they can provide better, more personalized interventions. Read two family's stories on how genomics help their understanding of autism and receiving personalized healthcare.
What environmental factors are associated with autism?
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, certain environmental influences may increase autism risk:
Advanced parental age
Prenatal exposure to air pollution or certain pesticides
Maternal obesity, diabetes or immune system disorders
Extreme prematurity or very low birth weight
Birth complications leading to periods of oxygen deprivation to the baby’s brain
What is Asperger syndrome?🧩
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF AUTISM🧩
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF AUTISM🧩
Asperger syndrome, or Asperger’s, is a previously used diagnosis on the autism spectrum. It was one of five forms of autism defined by the DSM-IV. In 2013, Asperger syndrome and the other autism-related diagnoses were folded into the broader autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 5 (DSM-5), now the DSM-5-TR.
The previous autism diagnosis categories included:
Autistic disorder
Childhood disintegrative disorder
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS)
Asperger syndrome
Rett syndrome
Although Asperger syndrome has been retired from use by medical professionals, some who received the diagnosis prior to 2013 still use the term and see it as an important part of their identity. Others prefer to refer to themselves as autistic. Both are correct; it is just a matter of personal choice.
Asperger syndrome symptoms
There is significant overlap in Asperger’s symptoms and ASD symptoms. Learn more about the symptoms of autism.
What is Asperger's called now?
Today, those who would have previously met the criteria for Asperger syndrome are diagnosed with level 1 ASD. There is no difference between Asperger's and autism level 1 diagnoses.
Learn more about level 1 autism and how it is diagnosed in the DSM-5-TR.
Autism Prevalence🧩
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF AUTISM🧩
Autism Prevalence🧩
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2023)
- 1 in 36 children in the U.S. have autism, up from the previous rate of 1 in 44.
- 1 in 45 adults in the U.S. have autism
- In the U.S., about 4 in 100 boys and 1 in 100 girls have autism.
- Boys are nearly 4 times more likely to be diagnosed with autism than girls.
- Autism prevalence is lower among white children than other racial and ethnic groups:
- White – 2.4%
- Black – 2.9%
- Hispanic – 3.2%
- Asian or Pacific Islander – 3.3%
These changes reflect an improvement in outreach, screening and de-stigmatization of autism diagnosis among minority communities.
*The CDC autism prevalence estimates are for 8-year-old children across 11 monitoring sites in the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network in 2020.
Diagnosis and early intervention
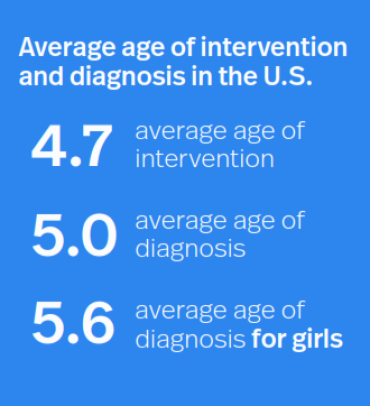
Source: National Survey of Children’s Health (NSCH) (2016-2019)
- Autism can be reliably diagnosed by a specialist by age 2, but the average age of autism diagnosis in the U.S. is 5 years.
- The average age of first intervention in the U.S. is 4.7 years.
- The average age of diagnosis for children in lower income households is 4.7 years compared to 5.2 years in higher income households.
The average ages of diagnosis and first intervention vary widely between states. See how your state compares.
Special Education
Source: U.S. Department of Education (2018-2019)
- 74% of autistic students in the U.S. graduate with a diploma, versus 86% of all students.
- 19% of autistic students in the U.S. graduate with a certificate.
- 8% of autistic students in the U.S. don't finish high school, versus 5% of all students.
View graduation rates in your state.
Employment

Sources: U.S. Department of Education (2014-2016), Bureau of Labor Statistics (2022)
- Only 21% of people with disabilities, including autism, are employed.
- Nearly 60% of people with autism in the U.S. are employed after receiving vocational rehabilitation (VR) services. These are state-provided services that help autistic individuals explore possible careers, find a job and secure needed accommodations in the workplace.
- 70% of eligible autistic individuals in the U.S. receive VR.
- 50% of autistic youth in the U.S. who receive VR begin those services in high school.
Dig deeper into VR outcomes across the U.S.
Healthcare Costs
Source: FAIR Health Inc. (2021)
The average costs of common autism services in the U.S. are:
- Adaptive behavior – $82.25
- Developmental screening – $165.95
- Emergency department – $1,397.22
- Physical therapy – $74.99
- Psychiatry – $253.40
- Speech/Language – $174.80
- Therapeutic behavioral – $175.44
🧩See the Latest News on Autism 🧩






🧩Welcome to Autism Drip! Shop now for the latest products.🧩
🧩Welcome to Autism Drip! Shop now for the latest products.🧩
🧩Welcome to Autism Drip! Shop now for the latest products.🧩
🧩Welcome to Autism Drip! Shop now for the latest products.🧩
🧩Welcome to Autism Drip! Shop now for the latest products.🧩
🧩Welcome to Autism Drip! Shop now for the latest products.🧩

THANK YOU FOR VISTING US
CHECK OUT OUR NEW PRODUCTS AND TELL A FRIEND TO TELL A FRIEND. YOUR SUPPORT ALLOWS US TO HELP SPREAD AWARENESS.
